Explore how VR special education is transforming learning with accessibility tools and therapeutic outcomes. This guide shows how VR special education supports both teachers and students in creating more inclusive classrooms. By focusing on VR special education practices, schools can integrate accessible technology that meets diverse needs. A complete guide to VR special education for schools highlights how these tools make learning more engaging and equitable.
Introduction
For a student with autism, practicing a simple social interaction like ordering a coffee can be overwhelming. For a student in a wheelchair, a field trip to a historical monument can be a logistical nightmare. What if there was a tool that could provide a safe, repeatable, and fully accessible alternative? This is the promise of VR special education, designed to make learning both supportive and inclusive. This guide explores how VR special education helps break down barriers for students with diverse needs, offering powerful therapeutic and educational outcomes. By the end, you’ll see how VR special education can empower teachers and learners, and why inclusive VR learning is becoming a cornerstone of modern special education programs.
What Is VR in Special Education?
VR special education involves using virtual reality technology to create tailored learning and therapeutic experiences for students with physical, cognitive, sensory, or emotional challenges. Unlike general apps, VR special education goes beyond standard tools by incorporating VR accessibility features and adjustable settings to build a controlled, safe, and supportive environment. With this approach, VR special education allows students to practice life skills, manage anxiety, and access curriculum content in ways that were once out of reach. Ultimately, VR special education provides opportunities for inclusion that traditional methods often cannot offer.
The need for such tools is significant. The World Health Organization reports that millions of children live with disabilities that can impact their learning. In 2025, technology is no longer just about engagement; it’s about equity. The future of **therapeutic VR in schools** lies in creating deeply personalized experiences that can adapt in real-time to a student’s sensory and cognitive needs, offering a new frontier for individualized education plans (IEPs).

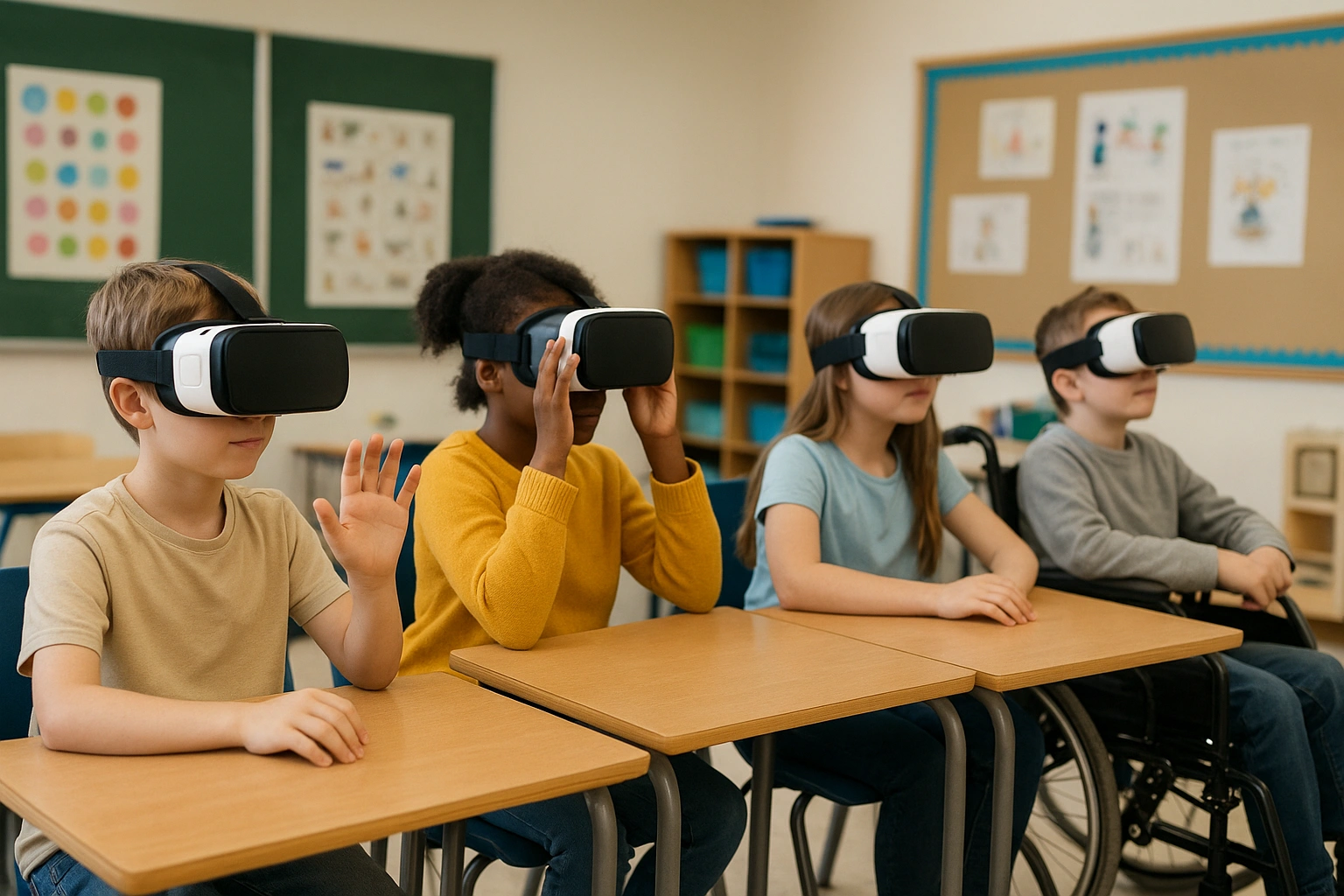
The Transformative Benefits of Inclusive VR Learning
VR special education offers unique advantages that directly address the challenges faced by many students in specialized programs. Through carefully designed activities, VR special education can remove barriers that limit participation in everyday learning. By creating safe spaces to practice essential skills, VR special education gives students confidence they can carry into real-life situations. In the end, VR special education becomes a powerful bridge toward more inclusive and meaningful education.
Create Safe Environments for Life Skills Practice
VR provides a safe, repeatable space for students, particularly those on the autism spectrum, to practice social and functional life skills without the anxiety of real-world consequences.
- Example: A student can practice crossing the street, navigating a grocery store, or having a conversation with a virtual character who provides gentle feedback.
- Benefit: Builds confidence and competence in a controlled setting, which can then be transferred to the real world.
Provide Accessible Experiences for All
For students with physical disabilities, VR can remove physical barriers, allowing them to participate in field trips and hands-on activities alongside their peers.
- Example: A student who uses a wheelchair can explore the Amazon rainforest or tour the International Space Station from their classroom.
- Benefit: Promotes inclusion and provides equitable access to learning experiences, regardless of physical ability.
Offer Controlled Sensory and Emotional Regulation
Therapeutic VR in schools can be a powerful tool for emotional regulation. Calming virtual environments can help students with anxiety or sensory processing disorders de-escalate and learn coping mechanisms.
- Example: A student feeling overwhelmed can enter a virtual “calm room” with soothing nature sounds, gentle lights, and guided breathing exercises. For more on lesson creation, see our guide to [VR lesson plans](https://primbononline.com/vr-lesson-plans/).
- Benefit: Empowers students with self-regulation tools and helps manage challenging behaviors in the classroom.
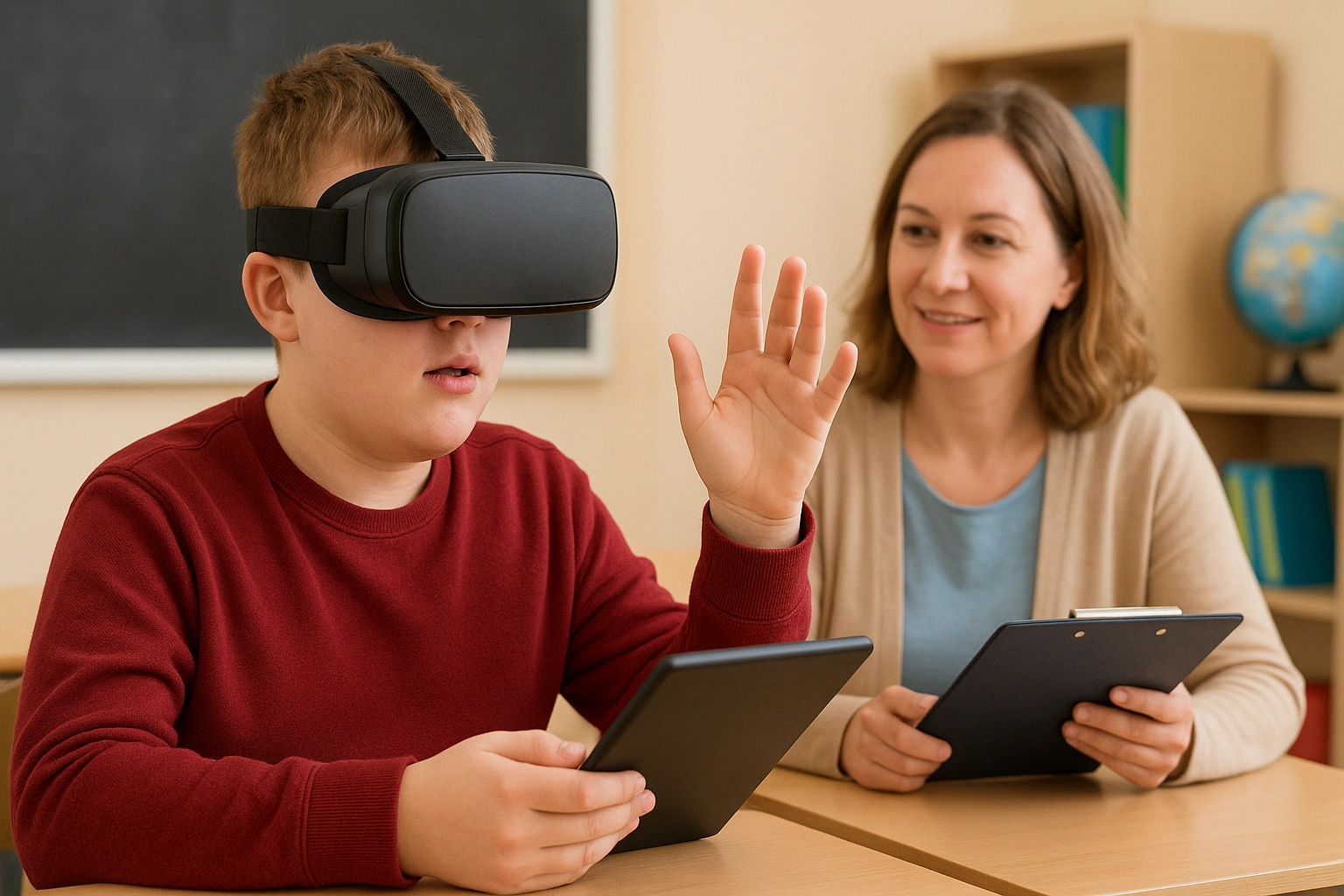
How VR Accessibility Tools Work
Inclusive VR learning is made possible by a combination of thoughtful software design and adaptive hardware.
- Adjustable Sensory Inputs: Software allows teachers or therapists to control the level of sensory stimulation, such as reducing background noise, simplifying visual complexity, or slowing down the pace of an activity.
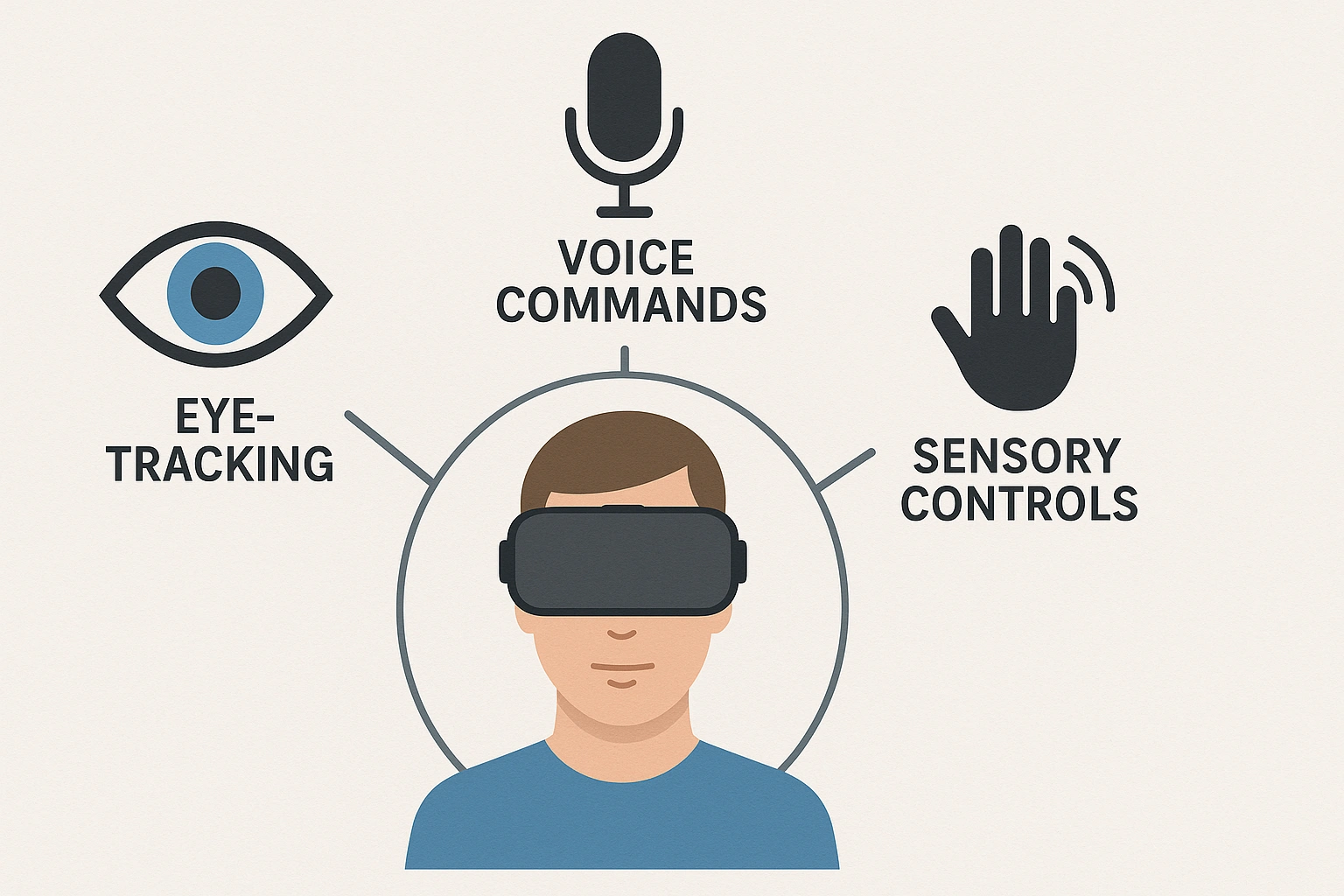
- Alternative Control Schemes: VR systems can be adapted for users with limited mobility. This includes eye-tracking for navigation, voice commands, or simplified single-button controllers.
- Predictable, Structured Content: Many therapeutic apps are designed with clear routines and predictable patterns to be reassuring for students who thrive on structure.
- Biometric Feedback (Advanced): Some cutting-edge systems can integrate with heart rate monitors to gauge a student’s anxiety level and automatically adjust the virtual environment to be more calming.
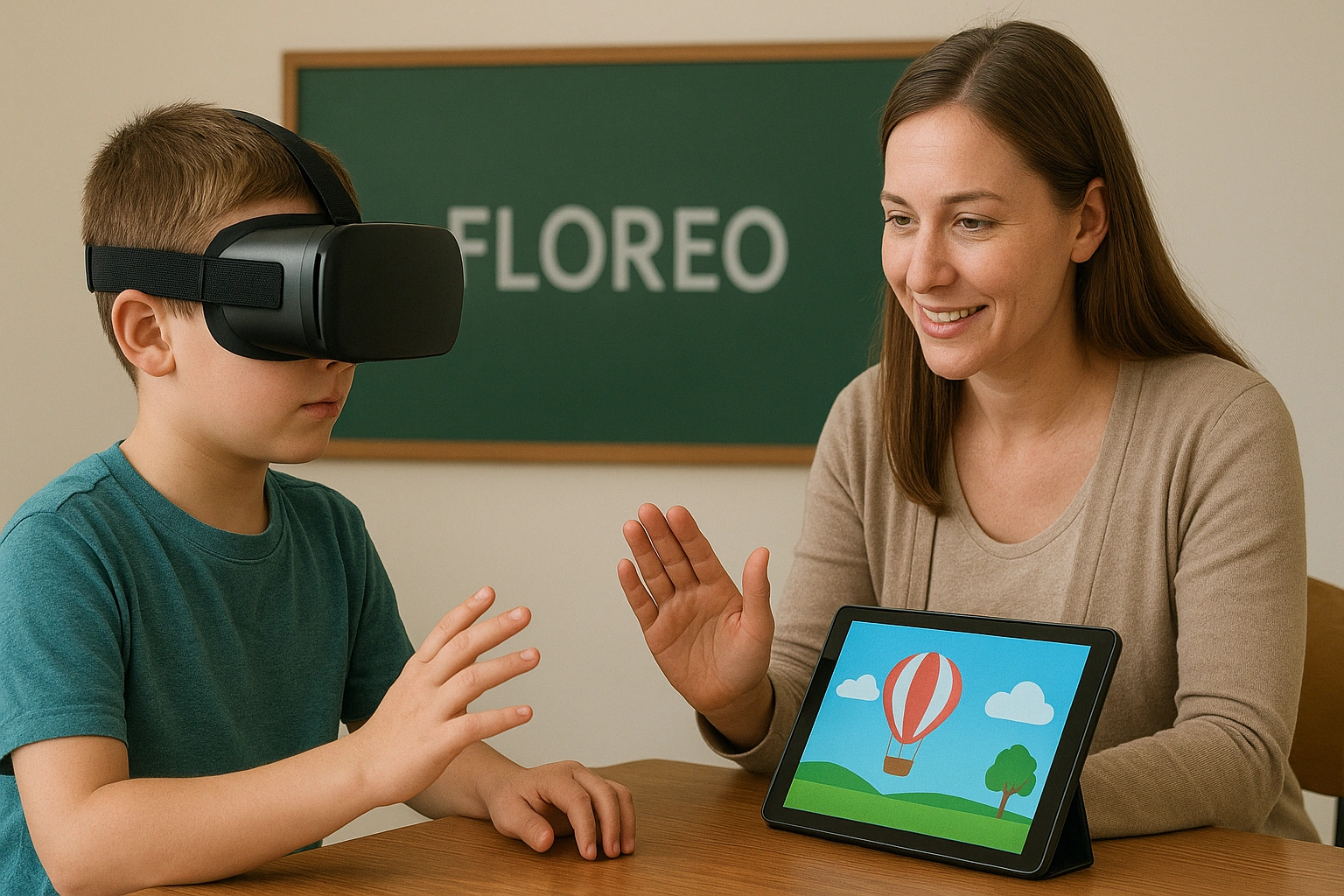
Product Spotlight: Floreo’s Virtual Therapy
To see this in practice, let’s look at **Floreo**, a leading platform in **therapeutic VR in schools**. Floreo offers a library of evidence-based lessons for individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), ADHD, and anxiety.
I explored one of their flagship lessons: “Street Crossing.” The experience is guided by a teacher or therapist on a linked tablet. They can control the traffic, introduce distractions, and trigger interactions. The student practices looking both ways and waiting for the signal in a completely safe environment. The therapist can see exactly what the student is looking at and provide real-time coaching. It’s a powerful, data-driven approach to teaching a critical life skill.

Pros & Cons of Specialized VR Platforms
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| ✅ Based on clinical research and evidence | ❌ Subscription-based and can be costly |
| ✅ Includes a companion app for therapist/teacher control | ❌ Content is highly specific and not for general curriculum |
| ✅ Provides data tracking and performance metrics | ❌ Requires training to use effectively as a therapeutic tool |
Comparison of VR Special Education Tools (2025)
Here’s a look at some of the top platforms for inclusive VR learning.
| Tool | Key Features | Pros | Cons | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Floreo | ASD & anxiety lessons, therapist-guided control | Evidence-based, data-driven | High cost, niche focus | School districts and therapy centers with dedicated ASD programs. |
| Google Earth VR | Virtual exploration of the entire globe | Free, provides immense sense of presence | No built-in accessibility features | Accessible field trips for students with physical disabilities. |
| Tripp | Guided meditation and mindfulness exercises | Calming, visually engaging | Subscription-based | Emotional regulation and creating “calm-down” corners in classrooms. |
Common Mistakes to Avoid in VR Special Education
To ensure a positive and effective experience, avoid these common mistakes:
- One Size Fits All: Assuming an app that works for one student will work for another. Personalization is key.
- Overstimulation: Putting a student into a visually or audibly “busy” environment without adjusting the settings first.
- Skipping the Introduction: Failing to properly and slowly introduce the headset and the experience to an anxious student.
- Using it as a Reward/Punishment: VR should be an integrated learning tool, not something to be earned or taken away.
- Ignoring Professional Input: Not collaborating with occupational therapists, speech pathologists, and other specialists when planning a VR session.
Expert Tips & Best Practices
Follow these tips from special education professionals:
- Start with Passthrough Mode: Let students get used to the headset’s weight and feel while still seeing their real environment.
- Co-Create the Experience: Involve the student in choosing the virtual environment or activity to give them a sense of agency.
- Mirror the Experience: Display what the student is seeing on a large screen so you can guide them and connect the virtual experience to the real world.
“For many of my students, the real world is unpredictable and overwhelming. VR allows me to give them a version of the world where the variables are controlled. It’s a place where they can practice and succeed, and that confidence is priceless.”
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Is VR safe for students with epilepsy or sensory sensitivities?
A: Caution is necessary. Always consult with a medical professional. For sensory sensitivities, start with very simple, low-stimulation apps in short bursts. Many platforms advise against use by individuals with seizure disorders.
Q: What are the best VR accessibility tools?
A: Key tools include software with adjustable sensory inputs, support for eye-tracking and voice commands, and simple, high-contrast user interfaces. Hardware-wise, lightweight headsets with balanced designs are crucial.
Q: How does therapeutic VR in schools help with anxiety?
A: It provides a tool for both exposure therapy (practicing anxiety-inducing situations in a safe way) and relaxation (using guided meditation and biofeedback apps to learn calming techniques).
Conclusion
Virtual reality is proving to be one of the most powerful assistive technologies of our time. In **VR special education**, it’s more than just a teaching tool—it’s a key that unlocks worlds of possibility. By focusing on **inclusive VR learning** and leveraging purpose-built **VR accessibility tools**, educators and therapists can create profound positive outcomes for students with diverse needs. As this technology continues to evolve, its role in building more equitable and effective learning environments will only grow. To follow the latest developments, keep up with tech resources like WIRED.
